文章目錄
懶人包
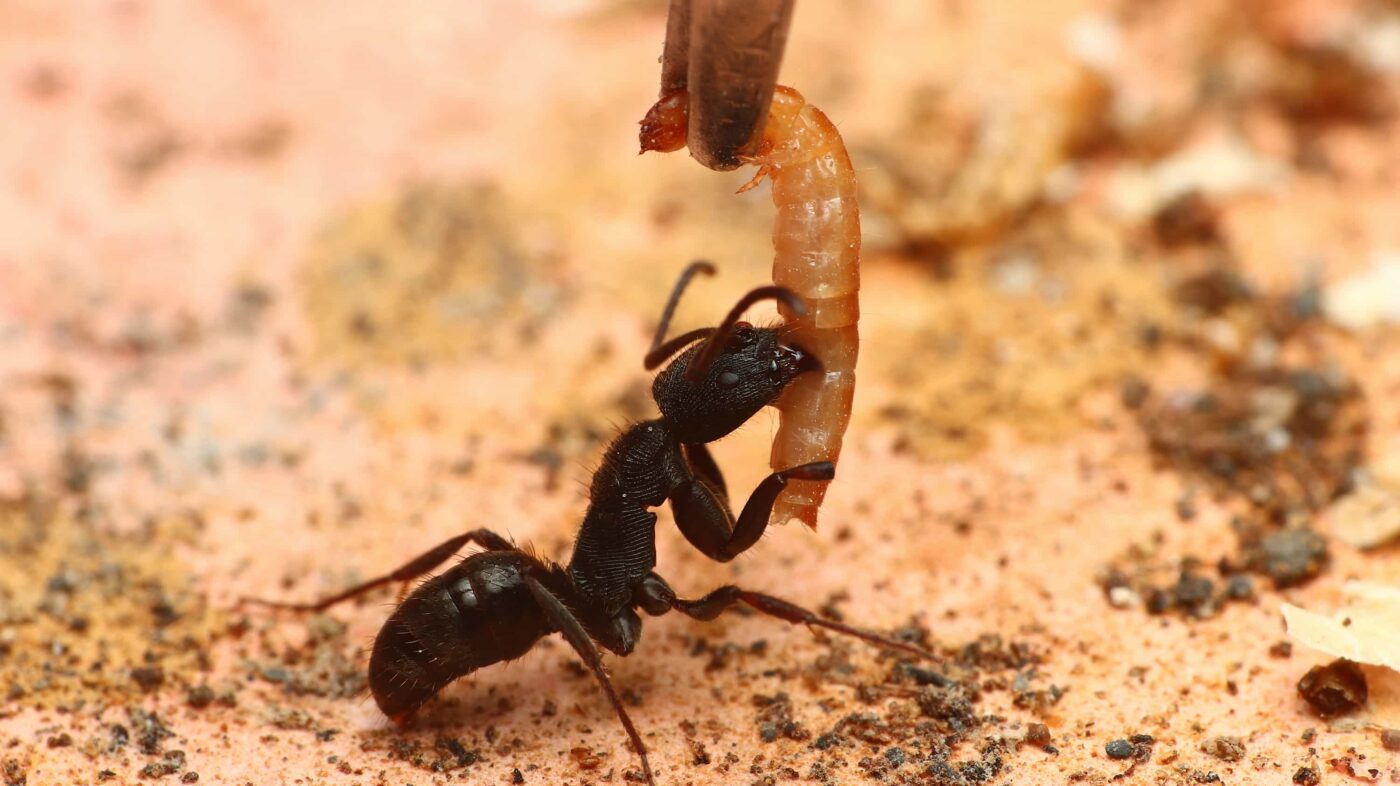
黃迷是一種優質的活餌來源,幼蟲含有 55% 的粗蛋白質,成蟲因外殼堅硬,僅留作繁殖之用。
飼養容易,繁殖方式為 3 大重點:
- 使用開放式塑膠容器
- 麥麩、麥片作為底材
- 保持乾燥、通風

黃迷的名字
黃迷只是一種簡稱,其學名為「九龍蟲」( Ulomoides dermestoides )
因體型比一般的麵包蟲更小,故被稱為「黃色迷你麵包蟲」,簡稱黃迷,本文將一律使用黃迷此綽號。

黃迷的資訊 | 成長周期
黃迷為鞘翅目 > 擬步行蟲科的昆蟲,成蟲有翅膀,但不會飛行。原生於亞洲的草原與沙漠之中,演變為人類穀倉內的害蟲,以穀物為生,後擴散至全球範圍,部分國家中,視黃迷為中藥材,認為其具有功效。
黃迷從卵到成蟲的過程,平均為 68 天。
成長過程共有四個階段,卵、幼蟲、蛹、成蟲,相較於麵包蟲而言,黃迷成長更快速。
卵
黃迷的卵經過 3 ~ 4 天孵化,非常小,人類肉眼幾乎不可見。
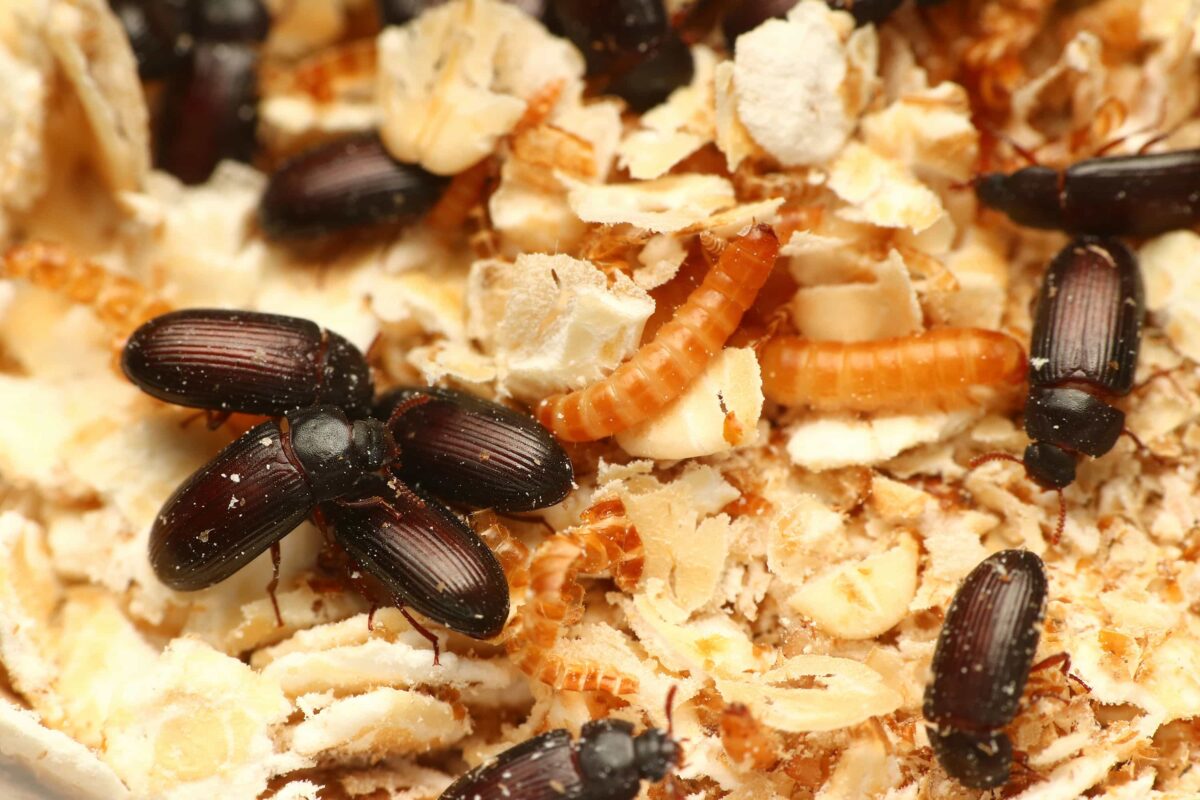
幼蟲
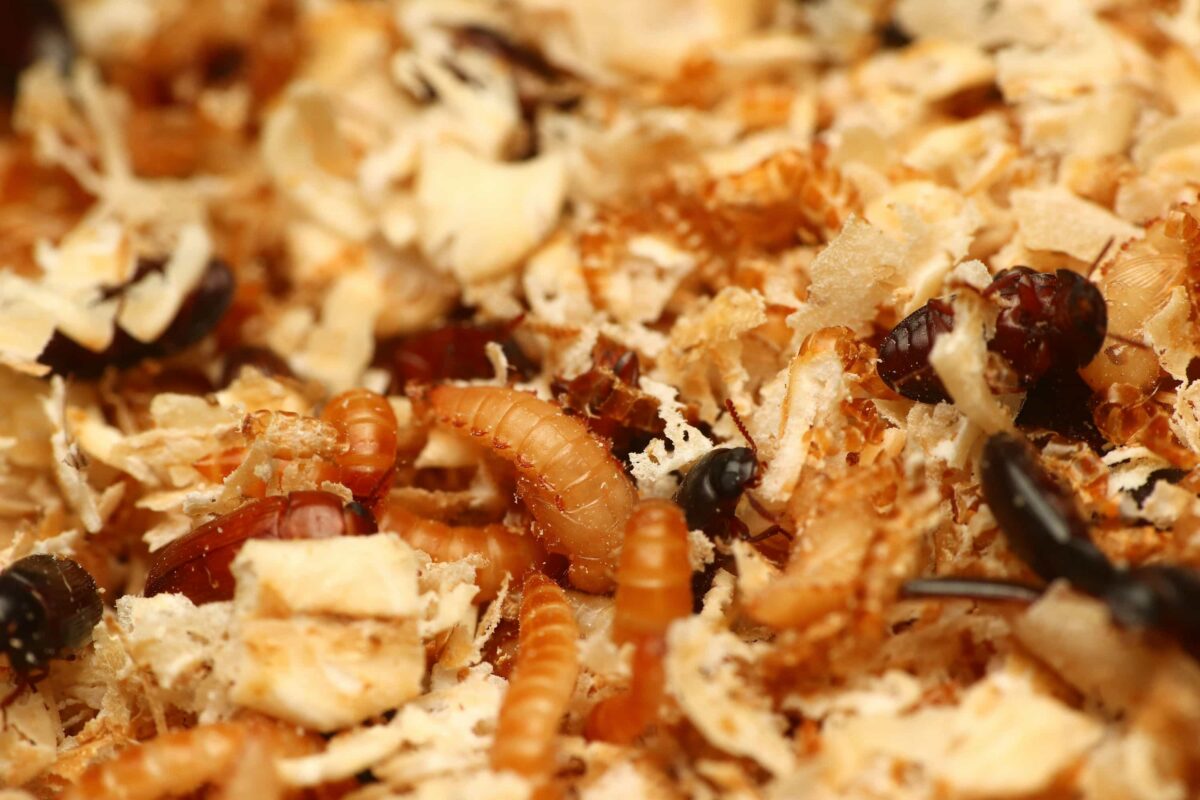
幼蟲階段為 60 天,共有 7 齡 ( 經歷 7 次蛻皮 ),接著進入蛹期,每一次的蛻皮,都會讓體型更大,剛蛻皮完成的幼蟲,顏色為乳白色, 1 天後逐漸變成黃色。
體型最大的幼蟲,約為 1.2 公分長,以麥麩、麥片、穀物為主食。
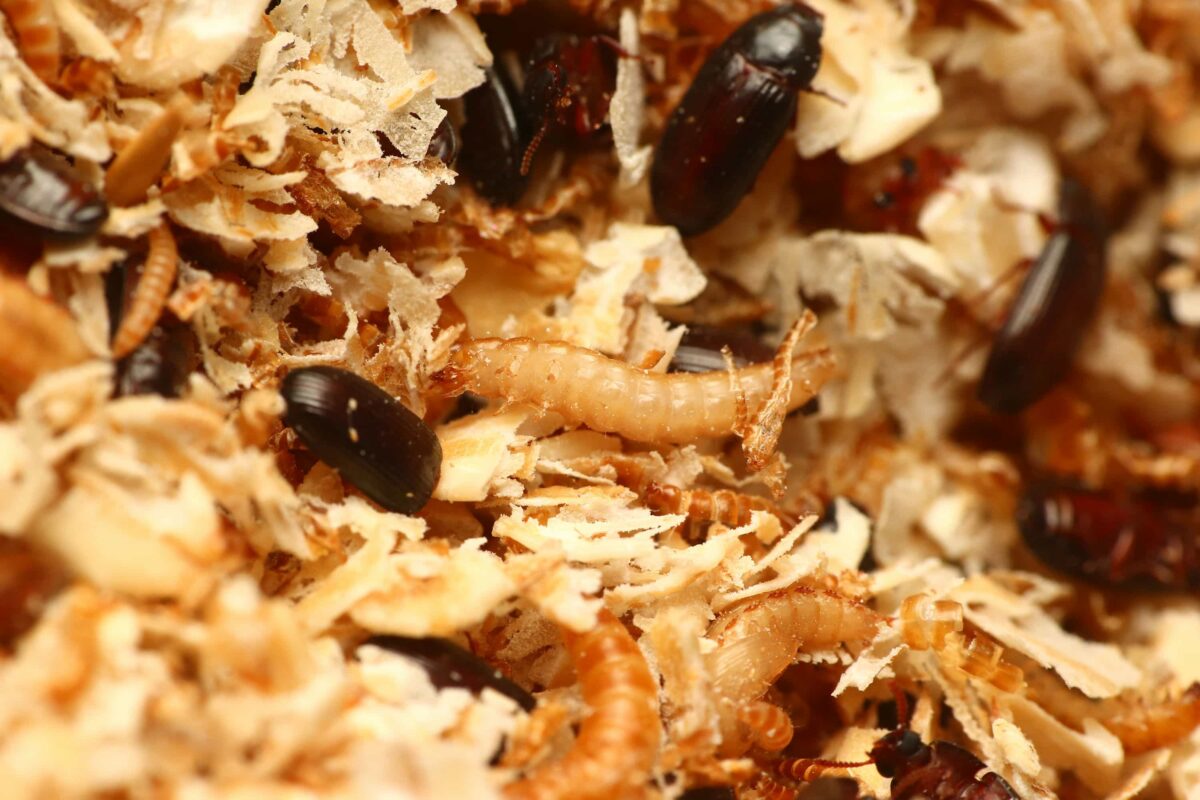



蛹
黃迷蛹經過 3 ~ 5 天,即會破蛹而出。
這期間,蛹的腹部 ( 尖端 ) 部分為可活動式的,但沒有移動能力,隨著即將破蛹,蛹的顏色會明顯逐漸加深,最終變為紅褐色。
正常的蛹,顏色為黃色至紅褐色,並且觸碰後會扭動,死掉或是受感染的蛹,則會發黑、不動,可藉此判斷蛹是否正常發育。
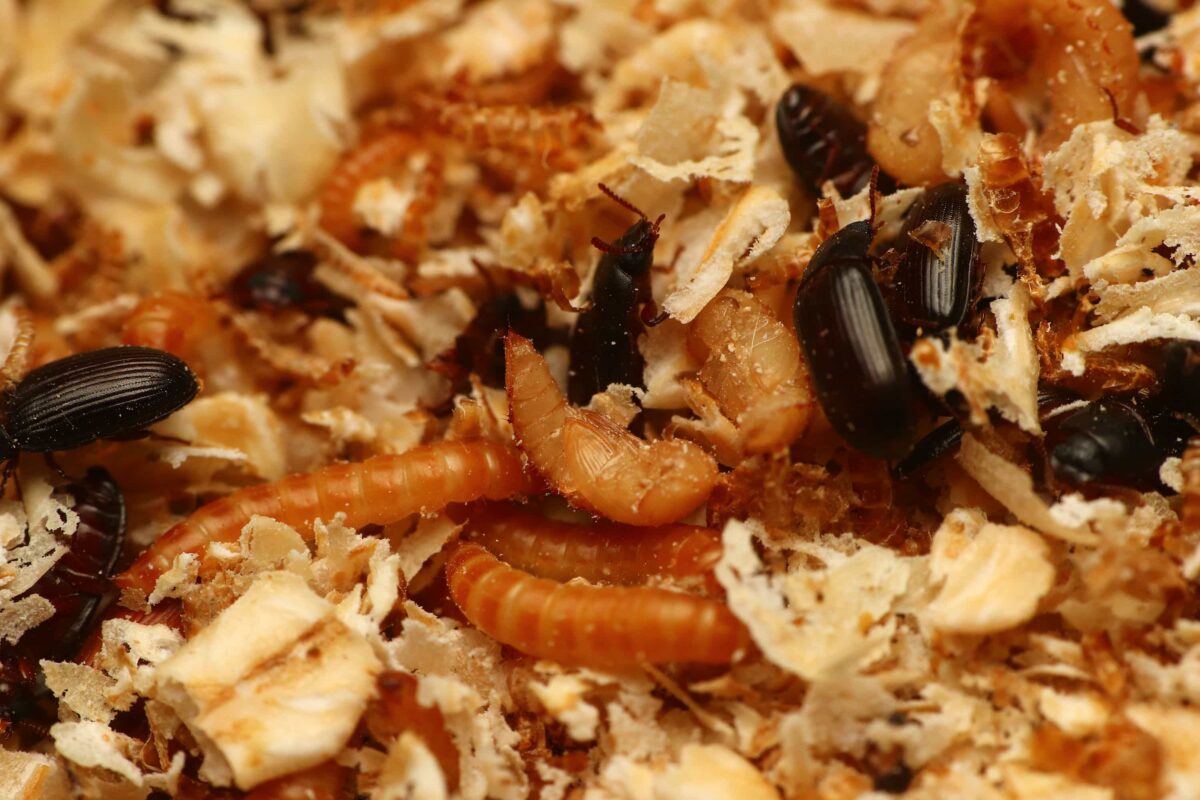

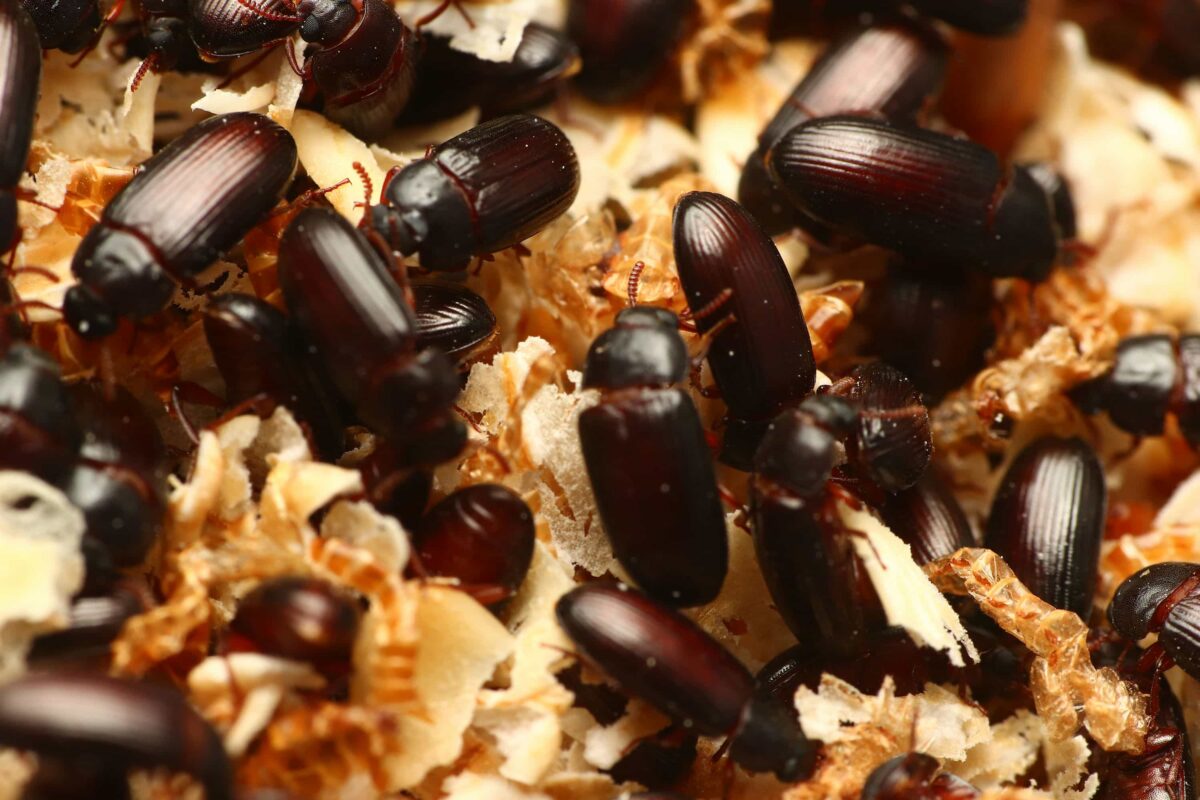
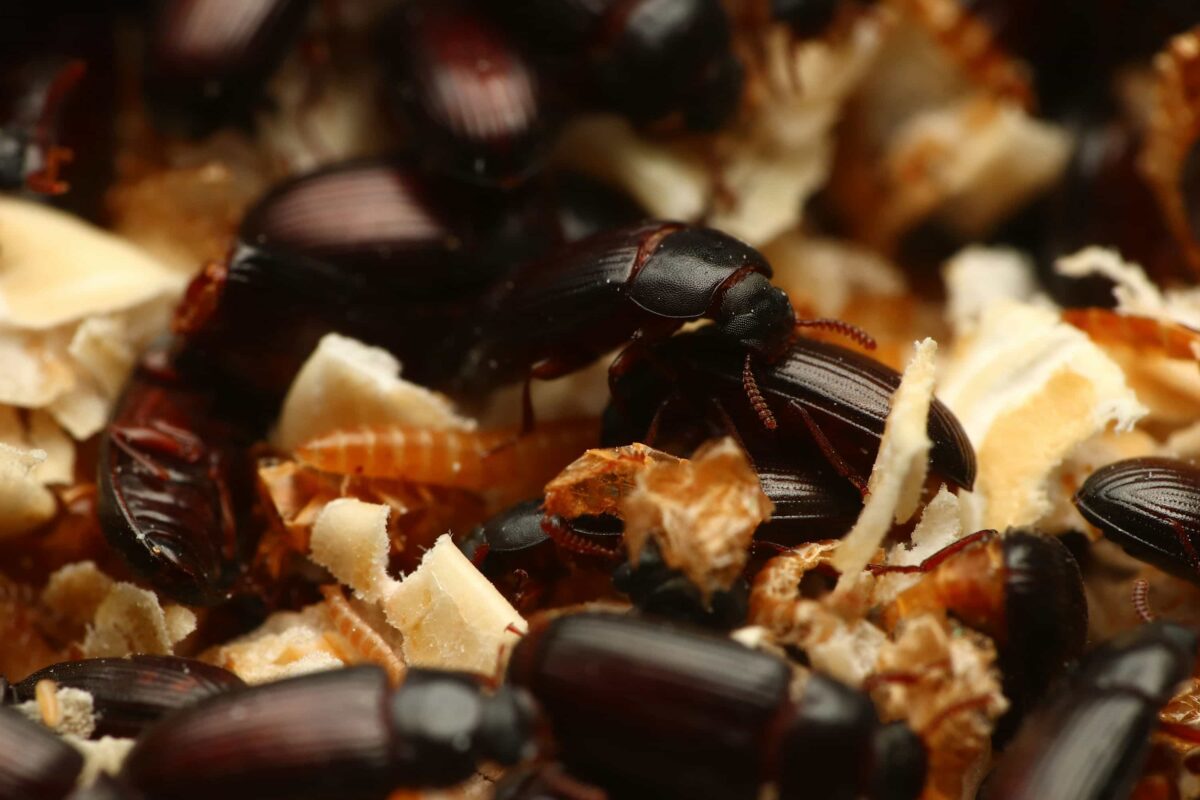
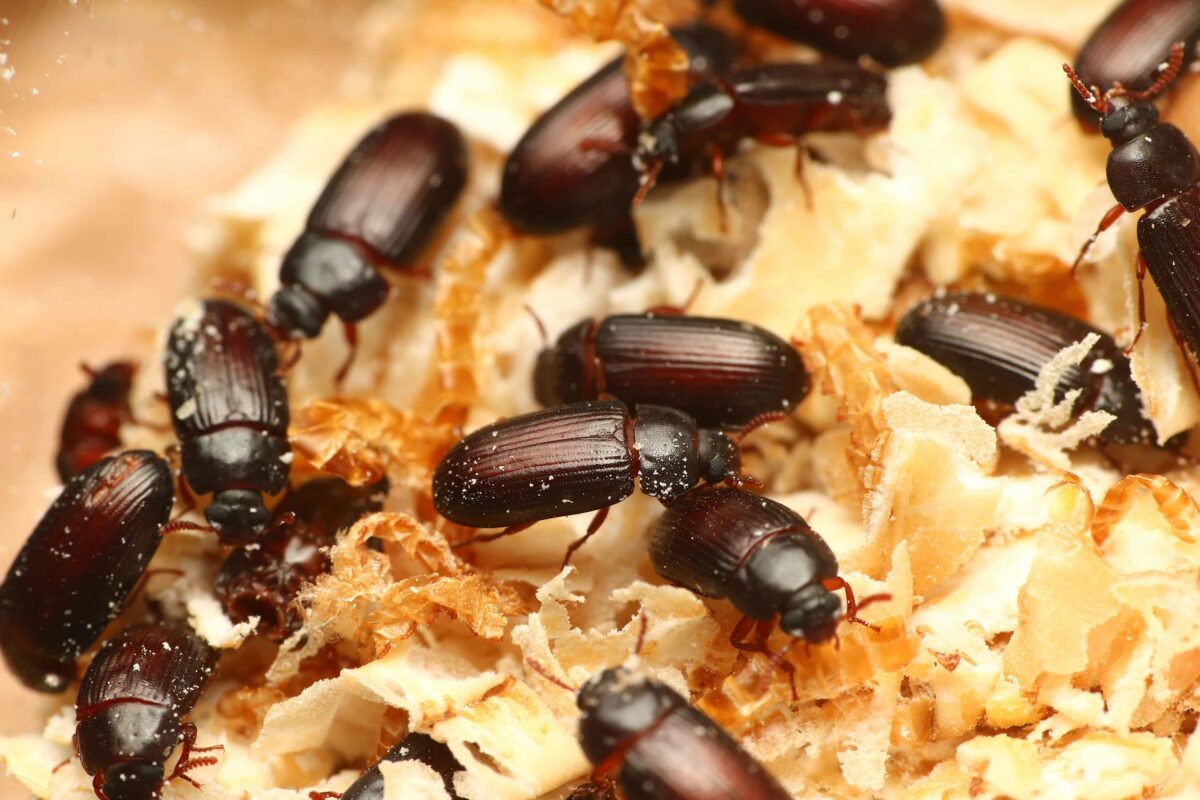
成蟲
黃迷成蟲壽命為 135 天,平均每隻雌性成蟲,可產下 261 顆卵。
成蟲階段,會不斷地與其他個體進行交配,交配後,雌蟲會將卵產在底材中,一次產下數十顆不等的卵。成蟲也會進食,與幼蟲相同,以底材 ( 穀物 ) 為主食。
雖然有翅膀,但黃迷成蟲並不具有飛行能力,也無法滑翔,攀爬能力弱,無法爬行於光滑的塑膠、玻璃表面。
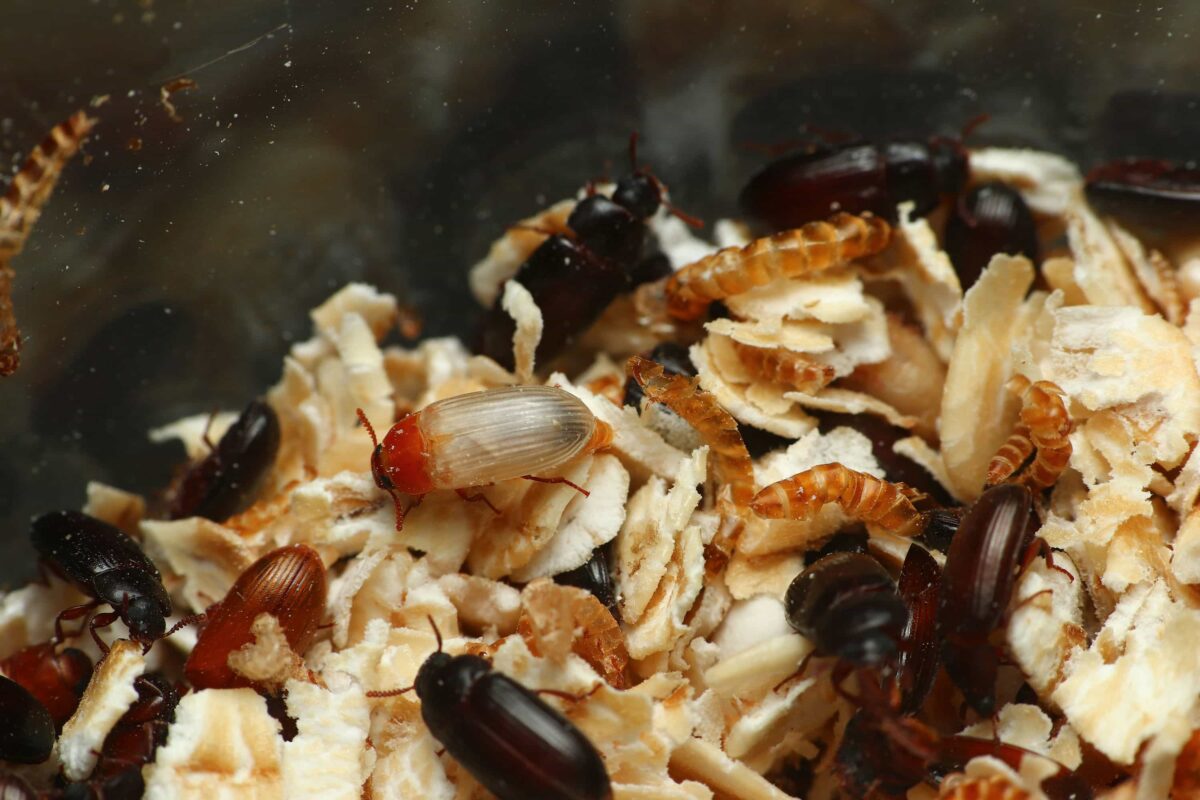
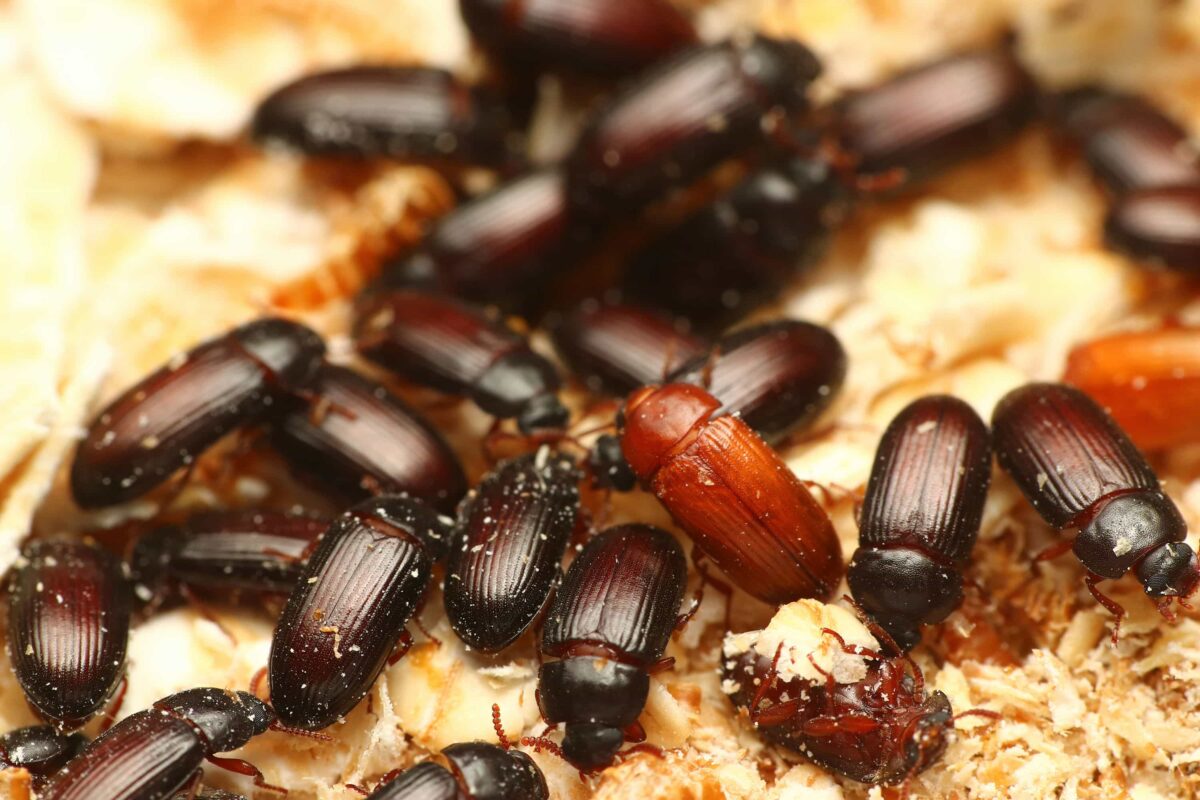



黃迷的營養成分
| 成分類型 | 黃迷成蟲 | 黃迷幼蟲 | 備註 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 粗蛋白 | 48.31 % | 54.95 % | 相對蛋白質含量高 |
| 粗脂肪 | 17.64 % | 18.24 % | 相較脂肪含量低 |
| 灰分 | 3.0 % | 2.8 % | 表示礦物質含量 |
| 總糖 | 31.05 % | 24.08 % | |
| 總胺基酸含量 | 39.03 g/100 g | 47.4 g/100 g | 胺基酸含量豐富,對健康有益 |
| 礦物質和微量元素 | 鋅高達 101.00mg/kg | 鋅高達 163.00mg/kg | 不含Cd、Hg、Pb,富含鋅 |
| 必需胺基酸指數 | 114.71 | – | 相對於一般蛋白質資源,黃迷的胺基酸質量更高 |
Ulomoides Dermestoides
Live Baits For Ants
黃色迷你麵包蟲(九龍蟲)是一種容易飼養的活餌,適合用於餵食給螞蟻、鼠、鳥即其他爬蟲類 不會飛、不會叫、不會臭,…
適合食用黃迷的寵物
黃迷幼蟲,因體型小,外皮薄,沒有攻擊性,並且營養含量極高,被視為小型寵物的絕佳活餌,尤其適合:螞蟻、跳蛛、蜘蛛、螳螂、鳥類、蜜袋鼯、小型鼠類、小型觀賞魚等

黃迷的飼養方式
繁殖黃迷時,最重要的因素,就是濕度、濕度、還有濕度!
飼養懶人包
- 使用廣而淺的塑膠容器
- 使用麥麩、麥片作為底材
- 底材保持 2 公分厚
- 飼養環境保持乾燥、通風
- 每個月過篩糞便
- 放置 PLAY

飼養環境
- 黃迷可在 18 ~ 32 度成長,但 24 ~ 28 度的飼養效果最佳
- 黃迷可在 50 ~ 90 % 濕度成長,但濕度 60 ~ 70 %為最佳
- 過乾,將導致卵和幼蟲乾死
- 過濕,將導致底材發霉、長螨蟲、腐爛病等
- 不用為黃迷加水,依靠空氣濕度就好
飼養容器
- 黃迷的幼蟲、成蟲,均無法攀爬光滑的表面,因此,使用透明的塑膠容器即可
- 黃迷需要乾燥、通風的環境,宜選用廣而淺的透明容器
- 容器深度,至少要 10 公分深
- 不須,也不必加蓋 ( 但透氣網可以 )
- 可以在大創、大賣場買到合適的容器,價格約 200 台幣以內
食物與底材
- 成蟲和幼蟲,都住在底材內,靠底材為食
- 底材應給予穀物為主,例如麥麩、麥片
- 底材建議至少要有 2 公分厚度
- 中國人會使用中藥材作為底材,但在台灣容易長螨蟲,不建議
- 添加額外營養食物,可以加快幼蟲生長、增加成蟲產卵量
- 使用 捕蟻人 所製造的 活餌菁英飼料可獲得更佳的效果
Special Insect Feed
For Insects As Feed To Ants
最好用的活餌飼料! 針對昆蟲餌料成長特別研發,經過大量實驗測試 證明能夠提升營養轉換率、增加蟲體免疫力、提高活…
水分控制
- 再次,濕度是關鍵
- 若在較乾燥的地區,可使用胡蘿蔔、馬鈴薯、蘋果,作為補充水分的食物,但切勿給過多
- 補水食物,一周一次,且控制在 1 天內可吃完的量
- 使用 捕蟻人 研發的 肥肥果凍 飼料,可以更好的控制給水量
- 肥肥果凍,可讓幼蟲體型大幅成長 ( 私心推薦 )
能讓幼蟲量大增的小技巧
- 成蟲會在底材內產卵
- 但更傾向使用產卵管,將卵產至狹小空間中
- 可在底材上鋪 濾水綿,供成蟲產卵
- 使用濾水綿,也可避免卵被幼蟲或成蟲誤食
- 這個小技巧聽我的準沒錯
過篩糞便
- 黃迷的糞便,會堆積在底材下方
- 糞便將產生氨和其他有害物質
- 糞便過厚、累積過久,將產生病原以及螨蟲
- 建議每個月使用篩網,過篩糞便
- 過篩後的糞便,還含有大量的卵和幼蟲,建議不要丟棄
- 將糞便獨立飼養,約一個月後又將出現數百條幼蟲
- 重複 2 ~ 3 次即可將該批糞便丟棄
同類互食
- 相較於麵包蟲,黃迷幾乎不會同類互食
- 除非是生活空間不足,例如飼養過於密集,或是底材太薄
- 蛹和卵是最容易被吃掉的
- 有足夠時間的話,可以將蛹獨立挑出來

繁殖密度控制
- 飼養密度不可過低和過高
- 密度太低,成蟲無法有效交配,產卵量少
- 密度過高,卵和蛹容易被誤食
- 建議達到一定程度就分裝飼養
- 以成蟲為目標,成蟲佔底材面積的 8 成以上即可分裝
FAQ
- 黃迷的飼養溫度和濕度範圍是多少?
最理想的溫度為26度,濕度在65%至70%之間。避免溫度超過30度或濕度超過75%,以免引起蟎蟲繁殖。 - 黃迷飼養的容器和底材有何特別要求?
需要深度至少10公分的塑膠容器,並在底部鋪設至少2公分厚的專用底材,保持適當的通風和濕度。 - 如何控制黃迷飼養的密度?
飼養密度應使底材表面積的60%至80%被佔用,避免過密或過稀,以免影響繁殖或導致疾病。 - 黃迷有哪些保健應用?
在台灣金門,黃迷被當作保健食品或中藥材。其糞便在中醫中也被視為有用的藥材。 - 如何避免飼養黃迷時出現蟎蟲問題?
保持理想的溫度和濕度範圍,避免過度潮濕,並注意飼養密度,可以有效減少蟎蟲的問題。